
CData Software Acquires Data Virtuality to Modernize Data Virtualization for the Enterprise
Data Virtuality brings enterprise data virtualization capabilities to CData, delivering highly-performant access to live data at any scale.
Explore how you can use the Data Virtuality Platform in different scenarios.
Learn more about the Data Virtuality Platform or to make your work with Data Virtuality even more successful.
Insights on product updates, useful guides and further informative articles.
Find insightful webinars, whitepapers and ebooks in our resource library.
Stronger together. Learn more about our partner programs.
Read, watch and learn what our customers achieved with Data Virtuality.
In our documentation you will find everything to know about our products
Read the answers to frequently asked questions about Data Virtuality.
In this on-demand webinar, we look at how a modern data architecture can help data scientists to be faster and to work more efficiently.
Learn more about us as a company, our strong partner ecosystem and our career opportunities.
How we achieve data security and transparency
Data lineage is a very hot topic these days, mostly driven by increasing regulatory requirements and data quality initiatives. Data lineage plays a critical role in better understanding the data itself: Where does the data come from? How was it modified and by whom? There are various perspectives and approaches out there. At Data Virtuality, we think that a comprehensive approach is needed for successful data lineage. The essential aspect is to make data lineage available together with the data. In this post we’ll highlight some of the major updates of the Data Virtuality Logical Data Warehouse 2.3
Starting LDW 2.3, you can see your data lineage with just one mouse click. Go to the number that you are interested in, click on the right button, and select “show data lineage”.
You will immediately see all the information about the data flow:
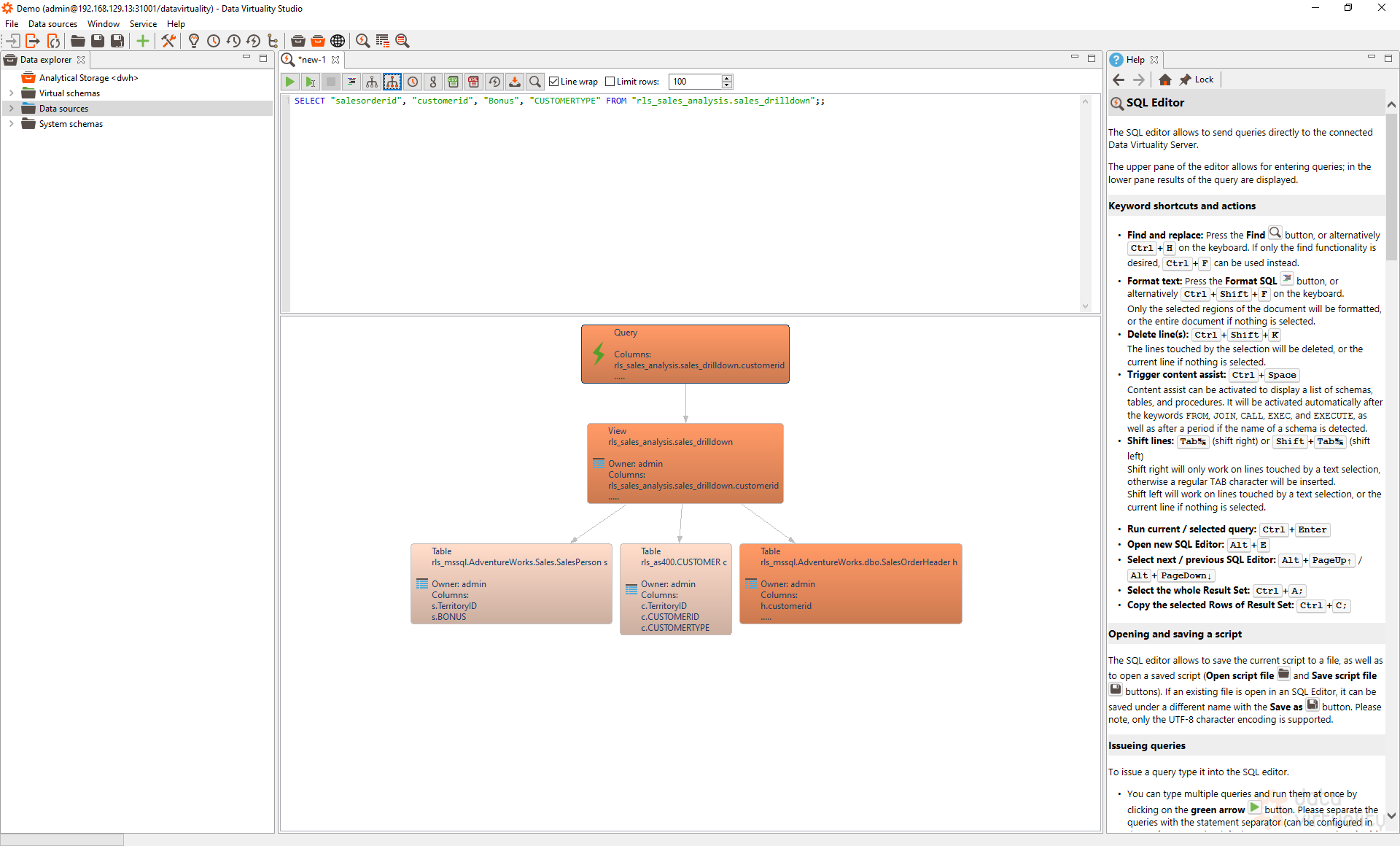
With this metadata information, you can instantly investigate if you see a red flag.
In today’s fast-changing business world, information became an actual production factor and data-driven decision-making an inevitable tool to withstand the growing competition across global industries and markets. Exploiting the power of BI/analytics and automating workflows is one way for companies to open new revenue streams while reducing costs by improving the efficiency of their daily processes.
And here lies the challenge. Nowadays, enterprise data is stored in different locations and comes in various, rapidly evolving forms such as:
Businesses are faced with increasing volumes of data accompanied by growing data variety and velocity. This ultimately leads to further challenges like achieving trustworthy data quality, time efficiency in data management and self-service capabilities for data users. Overcoming these challenges efficiently and effectively became crucial for modern enterprises’ success.
Next to data lineage, Data Virtuality introduces two features to advance the security management in the Logical Data Warehouse: row-based security, and column masking.
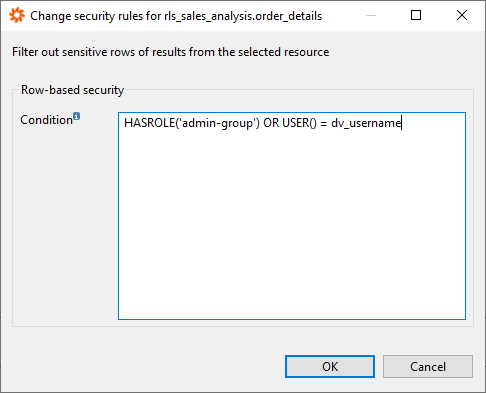
Row-based security allows to centrally control the data access. Based on preset conditions, data access for certain users/user groups can be determined. An example could be commission fees of salespeople. This kind of data is very sensitive and therefore needs special attention. With row-based security, the importance of data privacy can be reinforced.
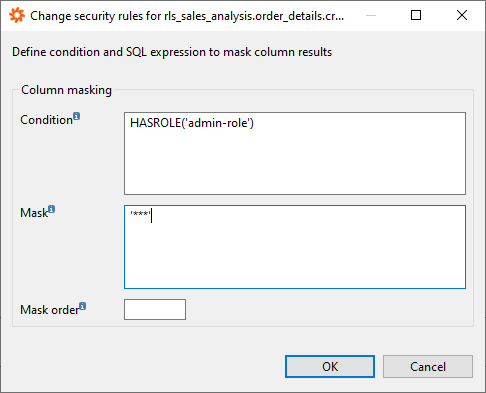
Lastly, you have a third security feature at your disposal in LDW 2.3: column masking. Column masking works similarly to row-based security, just vertically. This feature allows to restrict data access to whole columns. The masking feature allows the users to mask the data such as personal data incl. address, telephone number, and account and/or credit card number in a customized way, e.g. hashing, anonymizing or making it invisible. Besides the privacy aspect, this feature allows to increase efficiency as the users can focus on the relevant data only as the irrelevant data is not accessible.
With the web business data shop, Data Virtuality takes the self-service BI concept to the next level. This is a web-based access point to data for non-technical data consumers. The users get a first overview of what reports with the accompanying data sets are available. A short description gives a quick insight into what the specific data set is about. This could also include specific information about the data that the data consumer should be aware of. Furthermore, the data owner is shown to support data governance functionality.
Finally, each data set can be directly accessed through the preferred data consumption tool such as Tableau, Power BI, Excel, etc.
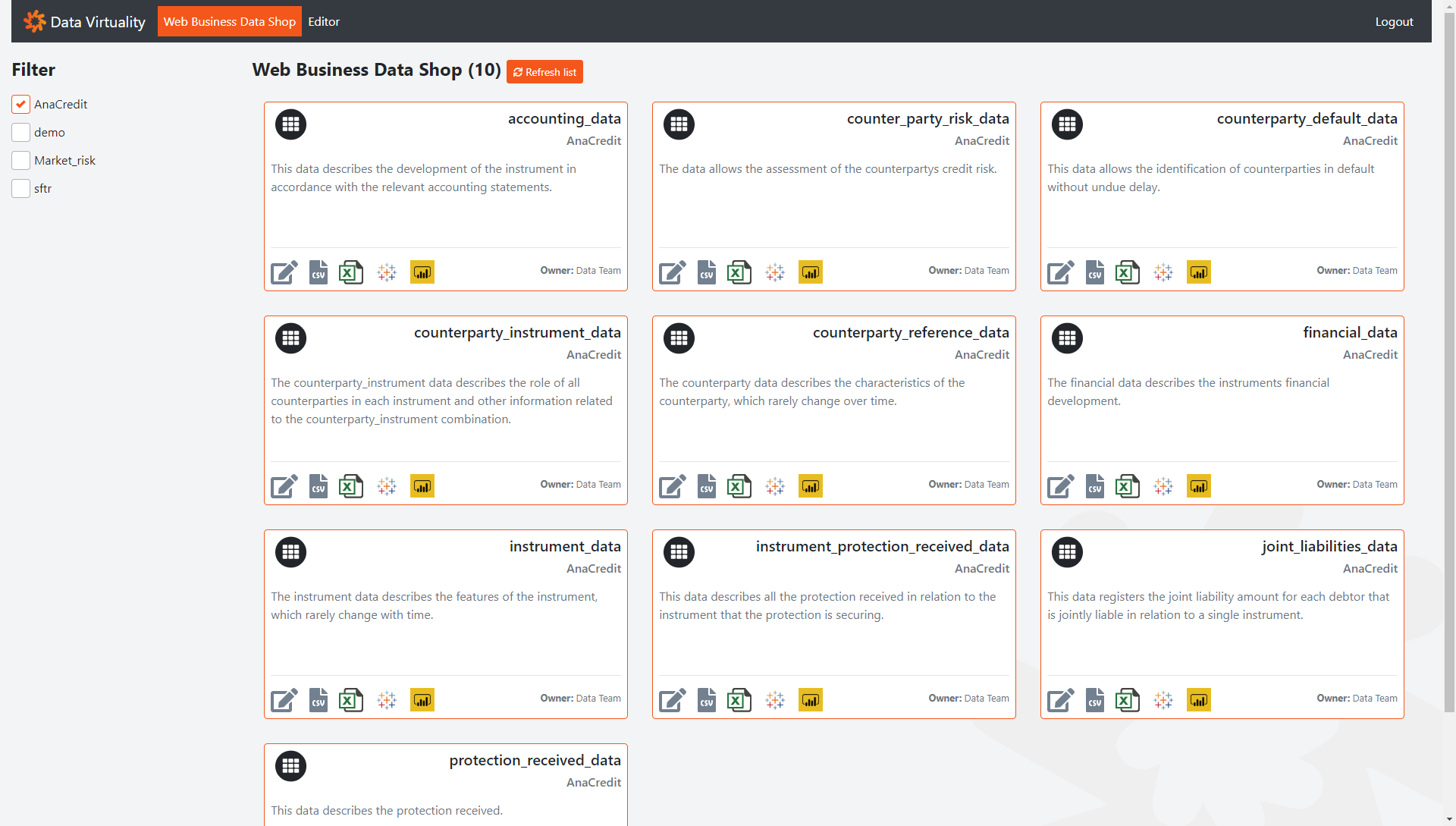
This feature is subject to permission settings. A sophisticated security model in the background ensures that the users can only see the tables for which they have permission.
Metadata visibility through JDBC/ODBC based on permissions will increase the convenience and improve user experience in the Logical Data Warehouse. It ensures that data consumers only see data for which they have permission. This drastically improves user experience as the data consumer doesn’t have to deal with blank fields or similar.
Book a demo and test the features of the Data Virtuality Logical Data Warehouse 2.3

Data Virtuality brings enterprise data virtualization capabilities to CData, delivering highly-performant access to live data at any scale.

Discover how integrating data warehouse automation with data virtualization can lead to better managed and optimized data workflows.

Discover how our ChatGPT powered SQL AI Assistant can help Data Virtuality users boost their performance when working with data.

While caching offers certain advantages, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. To comprehensively meet business requirements, combining data virtualization with replication is key.

Explore the potential of Data Virtuality’s connector for Databricks, enhancing your data lakehouse experience with flexible integration.

Generative AI is an exciting new technology which is helping to democratise and accelerate data management tasks including data engineering.
Leipzig
Katharinenstrasse 15 | 04109 | Germany
Munich
Trimburgstraße 2 | 81249 | Germany
San Francisco
2261 Market Street #4788 | CA 94114 | USA
Follow Us on Social Media
Our mission is to enable businesses to leverage the full potential of their data by providing a single source of truth platform to connect and manage all data.